1.3. Security¶
In production environments security, such as in authentication, authorization and transport encryption, is often desired. The Fast Data CSD supports SASL (Kerberos) and SSL Kafka authentication scenarios as well as TLS transport encryption. Authorization isn’t fully tested yet.
The CSD integrates deeply with Cloudera Manager and takes advantage of the built-in facilities to configure Kerberos and SSL with the less steps possible.
Important
In order to utilize security features succesfully we strongly advise cluster administrators to familiriaze with this document. We do automate most of the configuration but an administrator needs to know of certain workarounds and pitfalls in order to get the most out of the CSD.
Contents
1.3.1. Security Types and Status¶
1.3.1.1. Authentication¶
SASL (Kerberos) is the main authentication mechanism supported by both Kafka Brokers and Zookeeper [1]. Kafka Brokers also permit authentication via SSL client certificates.
As of Confluent version 3.2.x, all components (Schema Registry, Kafka Connect and Kafka REST Proxy) can use all authentication schemes to the brokers and the Zookeeper.
In addition, Kafka REST Proxy and Schema Registry offer client authentication for their APIs via SSL certificates. Kafka Connect does not support authentication to its API.
The current version of Kafka in addition to Kerberos (GSSAPI), supports two more SASL methods: PLAIN and SCRAM. Fast Data CSD currently supports only Kerberos for SASL authentication.
| [1] | As Kafka moves away from Zookeeper for storing its consumer offsets, it becomes much less taxing to Zookeeper service. Thus we chose to utilize Cloudera’s Zookeeper for Kafka’s coordination and service discovery tasks. The latest official Zookeeper (version 3.4) is the one featured in both CDH and Confluent packages and does not support SSL certificates for authentication but only Kerberos. SSL authentication is only added in the current, under-development, iteration of the software (Zookeeper 3.5.x) which is still in beta state and as only logical, should be avoided for use in production. Once Zookeeper 3.5 is added and supported by both Kafka and Cloudera, we will offer SSL authentication to it as well. |
1.3.1.2. Authorization¶
Authorization is implemented by Access Control Lists (ACLs), which are stored in Zookeeper by the default authorizer and enforced by the brokers. Third party authorizers are supported by Kafka.
Storing ACLs in Zookeeper means that we have to protect it as well. This is achieved by ACLs too, hence different ones, Zookeeper ACLs. Managing such ACLs is a much harder task, because these are enforced by Kerberos credentials and as of the time of this document, Kafka protects the data of its Znodes but permits writing new Znodes under protected ones. This can lead to various problems and unfortunately it doesn’t even have to be due to ill intent, it is easy for a user to accidentally create a topic using his/her own credentials. Fixing such mistakes can be cumbersome for administrators, due to the way Kerberos works.
Kafka moves towards a future where the clients will not ever have to access Zookeeper to perform tasks, so such issues may not be a problem in the future, but they are now. Although we include options for ACLs and perform some ACL management, we do not support ACLs at the moment due to their complex nature. Once we test them adequately we will provide a guide on how to safely use them and administer your services. Probably some manual intervention —documented here— will be needed to run an ACL setup. Until then we can help you through our support channels to implement ACLs.
Third party authorizers (such as Apache Sentry and Apache Ranger) may not rely on Zookeeper. In order to use such an authorizer you have to add its jar files to the broker’s classpath. You can achieve that by setting the CLASSPATH environment variable in the environment safety valve of the brokers. In the future we may provide third party authorizers as parcels.
The rest of the stack has limited support for ACLs as client to Zookeeper and the Brokers. The API endpoints of Schema Registry, Kafka REST Proxy and Kafka Connect do not offer authorization.
1.3.1.3. Transport Security¶
Transport security is handled by TLS/SSL listeners on the Brokers, the Schema Registry and the Kafka REST Proxy. Kafka Connect does not offer SSL for its server part but can use SSL to connect to the brokers.
As of Confluent Platform 4.0.x some workarounds and plaintext listeners are still needed, especially for the Schema Registry. They are documented in the schema registry section below.
1.3.1.4. Authentication Support Matrix¶
These are the possible authentication scenarios Confluent Platform supports. All can be setup and managed within the Fast Data CSD. Please note that TLS provides always transport encryption and optionally authentication via client SSL certificates.
Client ▼ | Server ► Zookeeper Broker Schema Registry Kafka Connect REST Proxy Broker NONE,SASL NONE,SASL,TLS not applicable not applicable not applicable Schema Registry NONE,SASL NONE,SASL,TLS NONE [2] not applicable not applicable Connect NONE,SASL NONE,SASL,TLS NONE,TLS [3] not applicable [4] not applicable REST Proxy NONE,SASL NONE,SASL,TLS NONE,TLS [3] not applicable not applicable Clients NONE,SASL NONE,SASL,TLS NONE,TLS NONE NONE,TLS
| [2] | Older Schema Registry versions couldn’t exchange data (run in master-slave configuration) via SSL. Whilst in 4.0 this issue is reported as fixed, a new bug was introduced, where a Schema Registry with only SSL listeners will fail to start (due to errors when checking the requested scheme). As such, Fast Data supports only unencrypted connections between Schema Registry instances. |
| [3] | (1, 2) Connections to an SSL’d Schema Registry from Kafka Connect and Kafka REST Proxy are limited to unauthenticated connections and only if the Schema Registry’s certificate is signed by a CA that is present in the JRE’s default truststore. |
| [4] | Kafka Connect workers on distributed mode do not exchange data, only configuration via zookeeper and kafka, so they don’t speak directly to each other. |
1.3.2. Kerberos (system-wide)¶
kerberos (SASL/GSSAPI) can be used to authenticate to the brokers and zookeeper;
it is well supported by the Fast Data CSD. You can enable it through the service
wide setting kerberos.auth.enable.
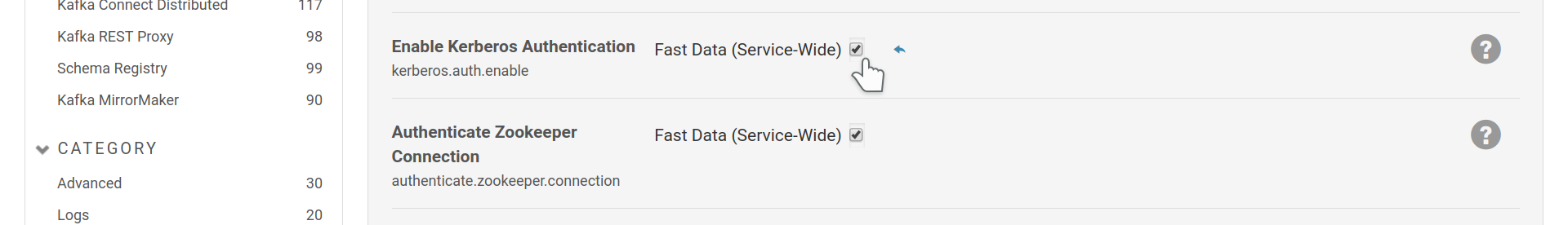
Enable Kerberos support.
This setting by itself instructs Cloudera Manager to issue keytabs to the Fast Data service roles and load them. Keytabs are files that contain Kerberos principals and encrypted keys. They are used by client or server applications to authenticate or provide authentication via a kerberos authentication service. In order to make use of them, you also have to add a SASL or a SASL_SSL listener to the brokers as described in the next section.
The credentials provided may be used to authenticate to zookeeper as well, which, as you may notice in the figure above, is the default behaviour for the CSD once Kerberos is enabled.
1.3.3. Broker Security¶
The Kafka Brokers support both SASL (Kerberos) and TLS/SSL client certificates for authentication, as well as TLS/SSL for transport encryption. As of Confluent Platform 3.2.x all components of the stack can interact with secured brokers.
A core concept in Kafka Brokers is that of a listener. A broker’s job is to serve requests from clients or other brokers. Brokers use listeners to listen for requests. Security is implemented at this level via four different types of listeners:
- PLAINTEXT
- No security, any client may connect.
- SASL_PLAINTEXT
- Authentication via supported SASL mechanisms (only GSSAPI/Kerberos for Fast Data).
- SASL_SSL
- Authentication via supported SASL mechanisms and transport encryption via TLS.
- SSL
- Transport encryption via TLS and optional authentication via client SSL certificates.
You can have up to one [5] instance of each type, so up to a total of four different listeners. Each one should use a different port. Setting up listeners is straightforward with Fast Data, using the configuration tab of the service; there are options to enable each type. These settings are in the Fast Data (Service-Wide) scope.
For listeners using SASL, Kerberos (system-wide) should be enabled as well. For listeners using SSL, SSL has to be configured for brokers and, depending on which listeners other roles (e.g Kafka Connect) will use, for these roles as well.
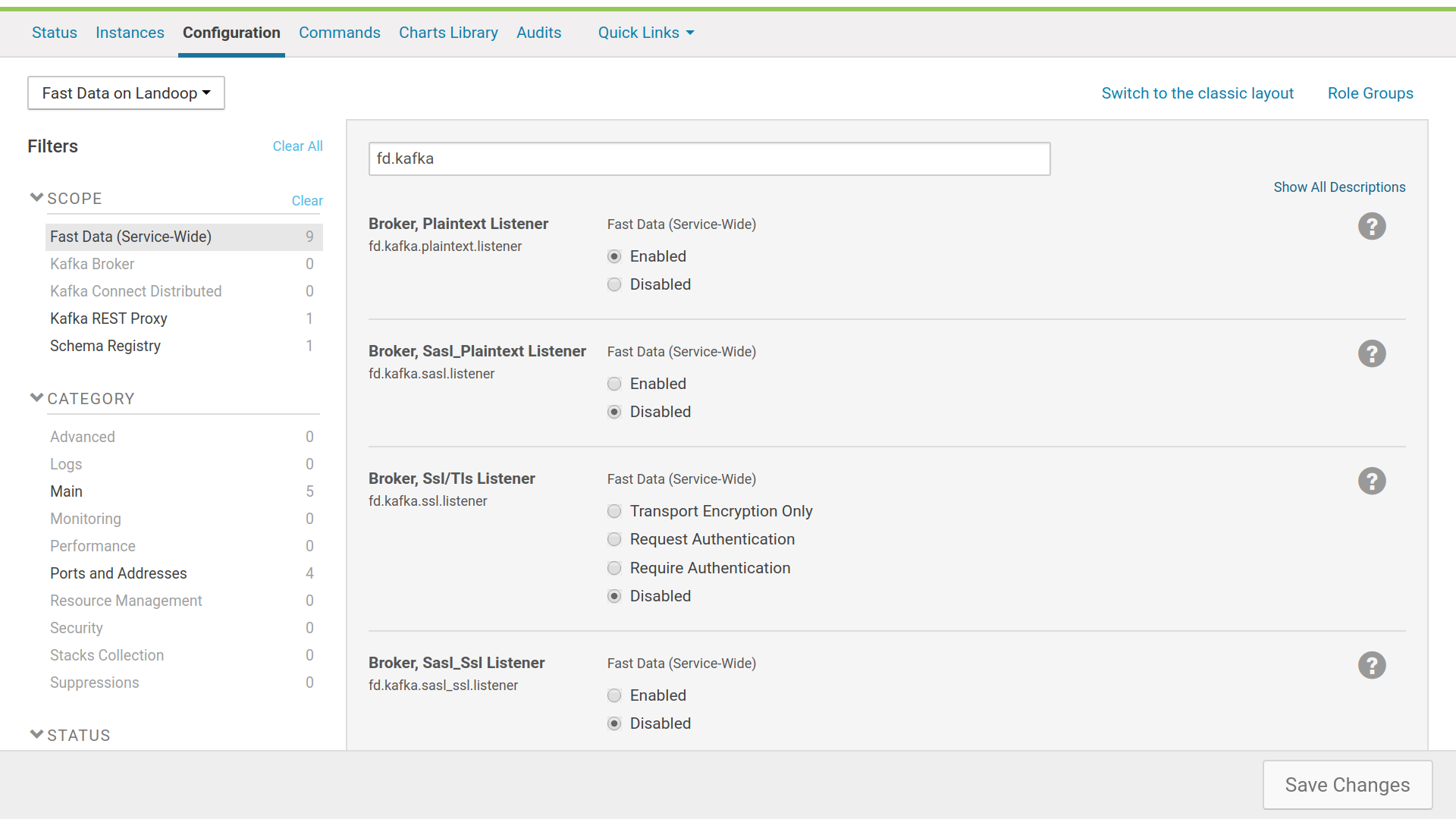
Setting up listeners with Fast Data
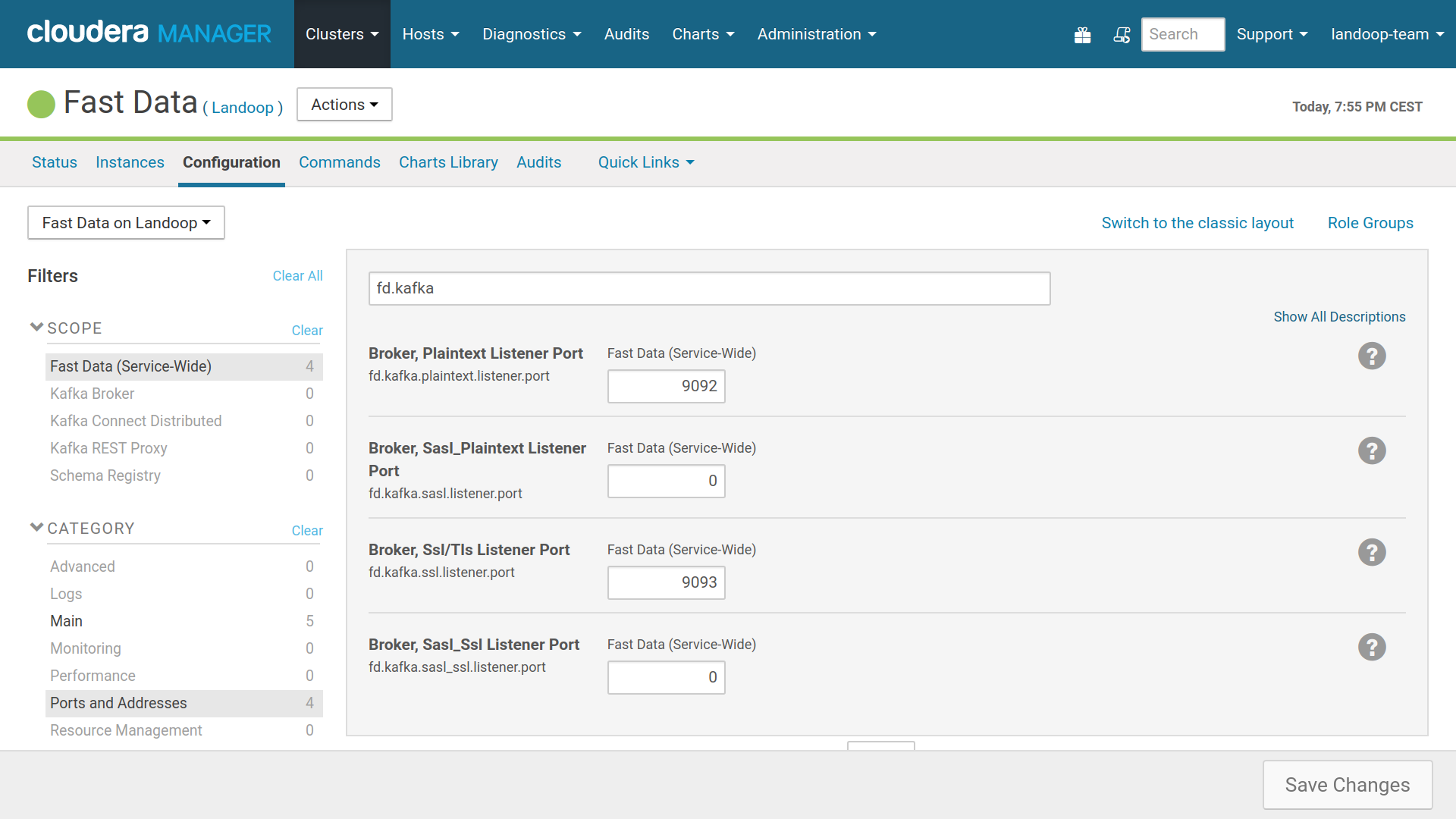
Enabled listeners should have a unique port
An important option when setting up more than one type of listener is the
preferred listener for service roles (fd.kafka.preferred.listener). This
sets which listener should Fast Data roles (Schema Registry, Kafka REST, Kafka
Connect) use to communicate with the brokers, as well as the communication
between brokers themselves. If set to AUTO, the first available listener in
the order of SASL_PLAINTEXT, PLAINTEXT, SASL_SSL and SSL will be used. SSL
options are at the bottom of the list because they have a significant
performance impact. If a specific type of listener is chosen, it should be
enabled as well.
Each role provides an override for this service-wide setting:
security.inter.broker.protocol for brokers, security.protocol for Kafka
Connect, client.security.protocol for Schema Registry and
kafkastore.security.protocol for Kafka REST.
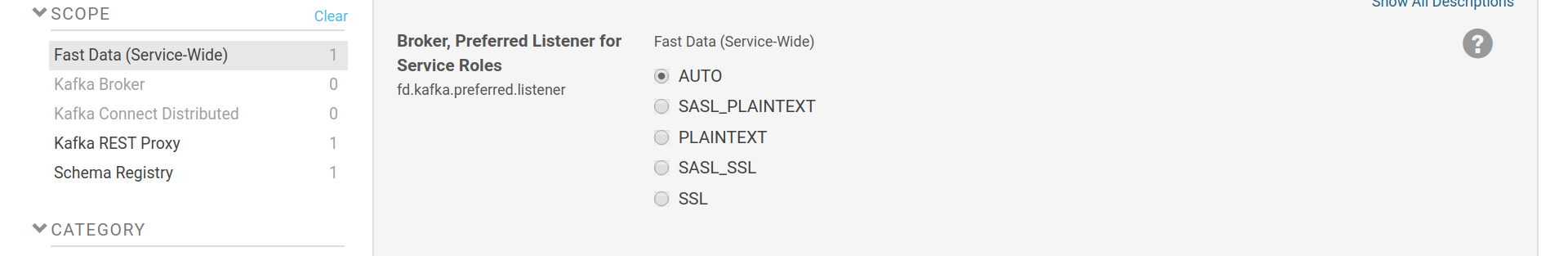
Preferred listener type for Fast Data services
Once you setup your listeners, you may want to checkout how to Verify Kerberos or how to Verify Brokers SSL Authentication.
| [5] | In Kafka 3.2.x the ability to have more than one instance of each listener type was added. This is convenient for dual traffic setups; one listener instance for your internal cluster network and a second one for clients from the external network. There are cases, such as cloud setups, where the internal network can be faster and cheaper than the external but inaccessible from external clients. Fast Data can support such setups but needs a more manual approach to the cluster setup. Please contact us for further information. |
1.3.3.1. TLS/SSL Setup¶
1.3.3.1.1. TLS/SSL Options¶
Before enabling a listener that uses SSL (types SASL_SSL and SSL), the broker has to be configured for SSL/TLS connections. You can find the related options in the Kafka Broker scope, at the security category.
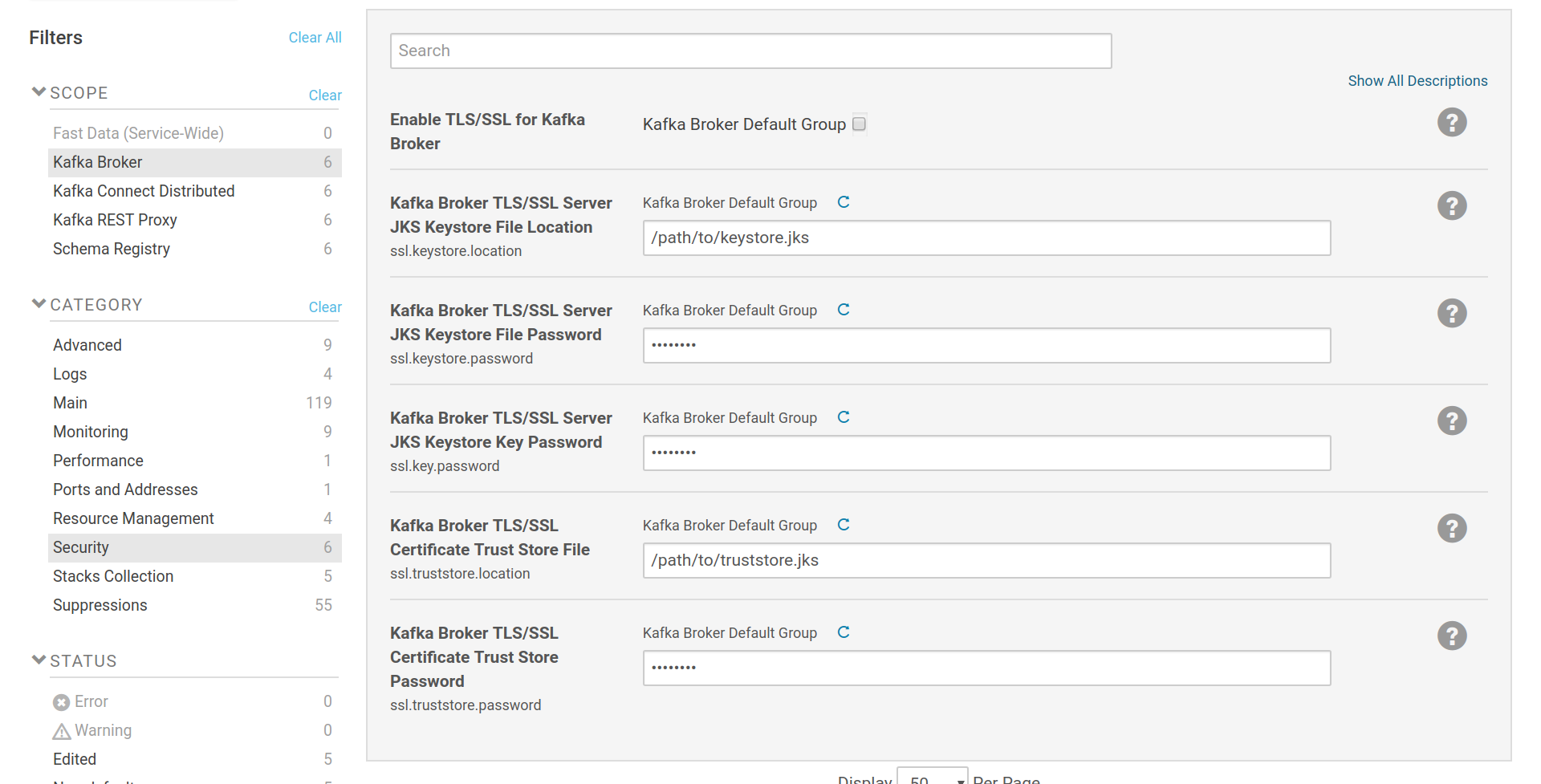
Broker SSL settings
The SSL configuration options are provided by Cloudera Manager and are
similar to any other role in CM that uses SSL.
The keystore settings (ssl.keystore.location, ssl.keystore.password,
ssl.key.password) are used to set the location and passwords of a java keystore
file which contains a SSL key and certificate pair. This pair is used by the listener
of the broker, as well as in the authentication process when the brokers are set
to communicate via SSL with SSL client certificate authentication. The
truststore settings (ssl.truststore.location, ssl.truststore.password)
are used to set the location and password of a java keystore file which contains
one or more certificates from trusted CAs. If
client authentication via SSL certificates is enabled, the certificate provided
by the client will be checked against these CAs. If the brokers are set to
intercommunicate via SSL, the client part of a broker will verify the
certificate provided by the listener of another broker against the CAs in its
truststore. Keystore and truststore can be the same file. Please note that the
option Enable TLS/SSL for Kafka Broker isn’t used. It is provided by Cloudera
Manager but the way Kafka makes use of SSL, does not require its setting.
Important
If a truststore isn’t set, the broker will fall back to the system truststore. This truststore most likely contains certificates from trusted CAs like such as Comodo or Let’s Encrypt, so anyone with a certificate from these companies may connect to your brokers.
1.3.3.1.2. SSL Listener Configuration¶
The SSL listener has various modes of operation. Transport Encryption Only
will set ssl.client.auth to none, which mean SSL will only be used
to protect the communication between client and broker. Request Authentication
will set the broker to offer optional authentication via SSL certificates.
Kafka developers discourage the use of this mode. Require Authentication
will let only authenticated clients to communicate with the broker. You may
refer to Kafka’s SSL Security documentation for more details.
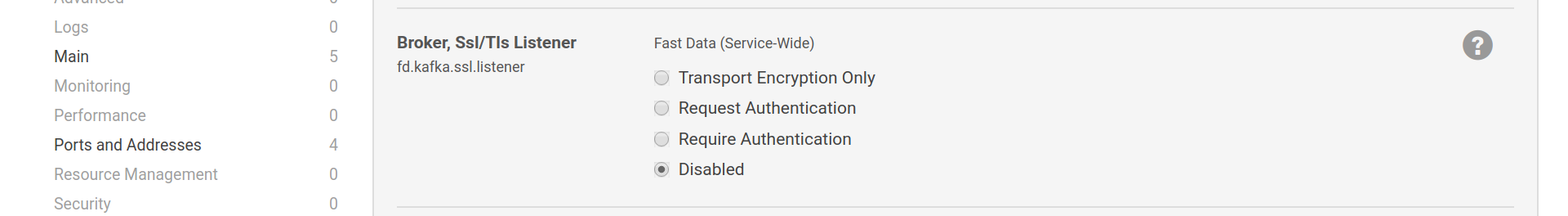
SSL listener configuration
Important
TLS/SSL can have a substantial impact in the performance of your Kafka cluster, maybe up to 30% or even more. You may want to setup a PLAINTEXT or a SASL_PLAINTEXT if there are roles or clients in your setup that can skip transport encryption.
1.3.3.2. Inter Broker Communication¶
You can set the protocol the brokers will use to communicate with each other via
fd.kafka.preferred.listener and security.inter.broker.protocol. The
latter takes precedence. If set to AUTO, then the former is used. If both are
set to AUTO, then the first available listener in the order of SASL_PLAINTEXT,
PLAINTEXT, SASL_SSL, SSL will be used. If an explicit listener is set yet not
enabled for the broker, then the broker will fail to start and will print the
error in the stdout log of the start command.
The brokers communicate via the same listeners that are available to clients. Due to replication, they may exchange large quantities of data at high throughput. It is often advised to avoid TLS/SSL for inter-broker communication due to the performance impact.
1.3.3.3. Client Roles Communication¶
Schema Registry, Kafka Connect and Kafka REST can connect to any type of broker
listener. Each has its own configuration option on which type of listener to
use: client.security.protocol, security.protocol,
kafkastore.security.protocol. If these are set to AUTO (the default
setting), then the setting in the service wide configuration
fd.kafka.preferred.listener will be used.
For connecting to a PLAINTEXT listener, no additional settings are needed.
For SASL_PLAINTEXT, service wide option kerberos.auth.enable should be
enabled. For SSL and SASL_SSL, TLS/SSL should be configured for each
role, similar to how the Broker role is setup. More information can be found
below, on each role’s respective section.
1.3.4. Schema Registry¶
Schema Registry provides support for TLS/SSL to its server component, either just for server validation and transport encryption, or additionally as an authentication mechanism via client certificates. The concept of listeners applies here as well, albeit with only two schemes: http and https. Due to certain issues (described in the subsections below) with the current iteration of Schema Registry, it is mandatory to enable both type of listeners when security is required. The http listener will be used by the Fast Data roles and the https by your clients.
The client component (Kafka consumer and producer) can connect to the brokers via any authentication mechanism provided by them.
1.3.4.1. Listener Configuration¶
Schema Registry’s listener settings are part of the Fast Data service-wide
scope. Listeners can be enabled via fd.registry.listener.http and
fd.registry.listener.https. Preferred listener for service roles (Kafka
Connect and Kafka REST) can be set via fd.registry.listener.preferred. If
left to AUTO, then the http listener will be used if it is enabled.
The https listener can be set to either provide only transport encryption or
to request authentication via SSL client certificates as well.
Please always keep enabled the http listener so it can be used by the Fast Data roles. Check Why a http listener is needed to understand the reason behind this issue. If security is needed, the http listener will have to be protected from client access by other means (e.g firewall).
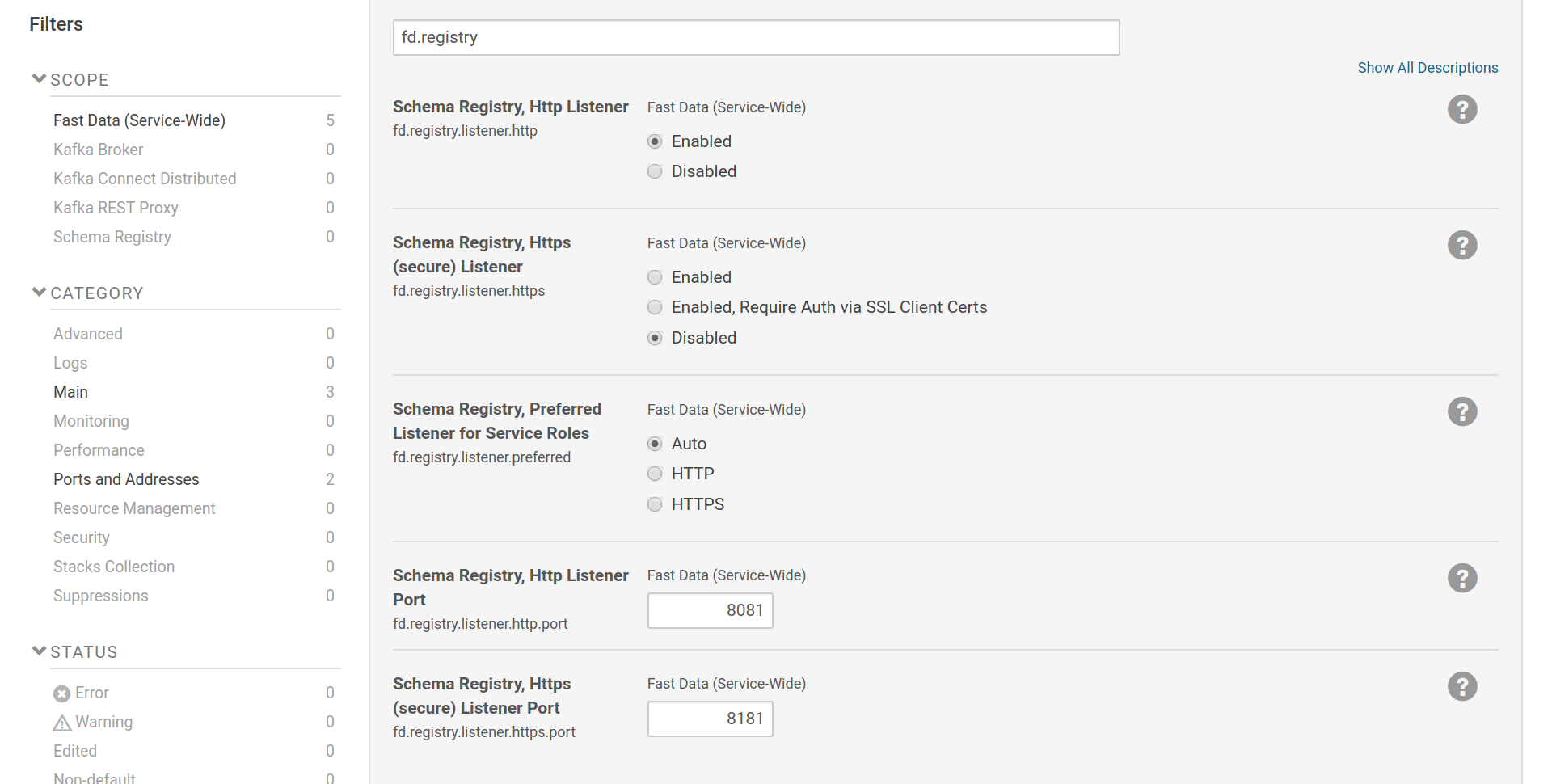
Settings for Schema Registry listeners
1.3.4.2. TLS/SSL Configuration¶
The SSL configuration options are provided by Cloudera Manager and are similar to any other role in CM that uses SSL. The SSL settings for the listener part are common with the settings for the client (consumer/producer) part. This can be overriden by a safety valve [6] .
The keystore settings (ssl.keystore.location, ssl.keystore.password,
ssl.key.password) are used to set the location and passwords of a java
keystore file which contains a SSL key and certificate pair. This pair is used
by the https listener, as well as in the authentication process when the Schema
Registry is set to communicate with the Brokers via SSL client certificate
authentication. The truststore settings (ssl.truststore.location,
ssl.truststore.password) are used to set the location and password of a java
keystore file which contains one or more certificates from trusted CAs. If client authentication via SSL certificates is
enabled, the certificate provided by the client will be checked against these
CAs. If set to communicate with the brokers via SSL, the kafka client will
verify the certificates provided by the brokers against the CAs in its
truststore. Keystore and truststore can be the same file. Please note that the
option Enable TLS/SSL for Schema Registry isn’t used. It is provided by
Cloudera Manager but the way Fast Data makes use of SSL, does not require its
setting.
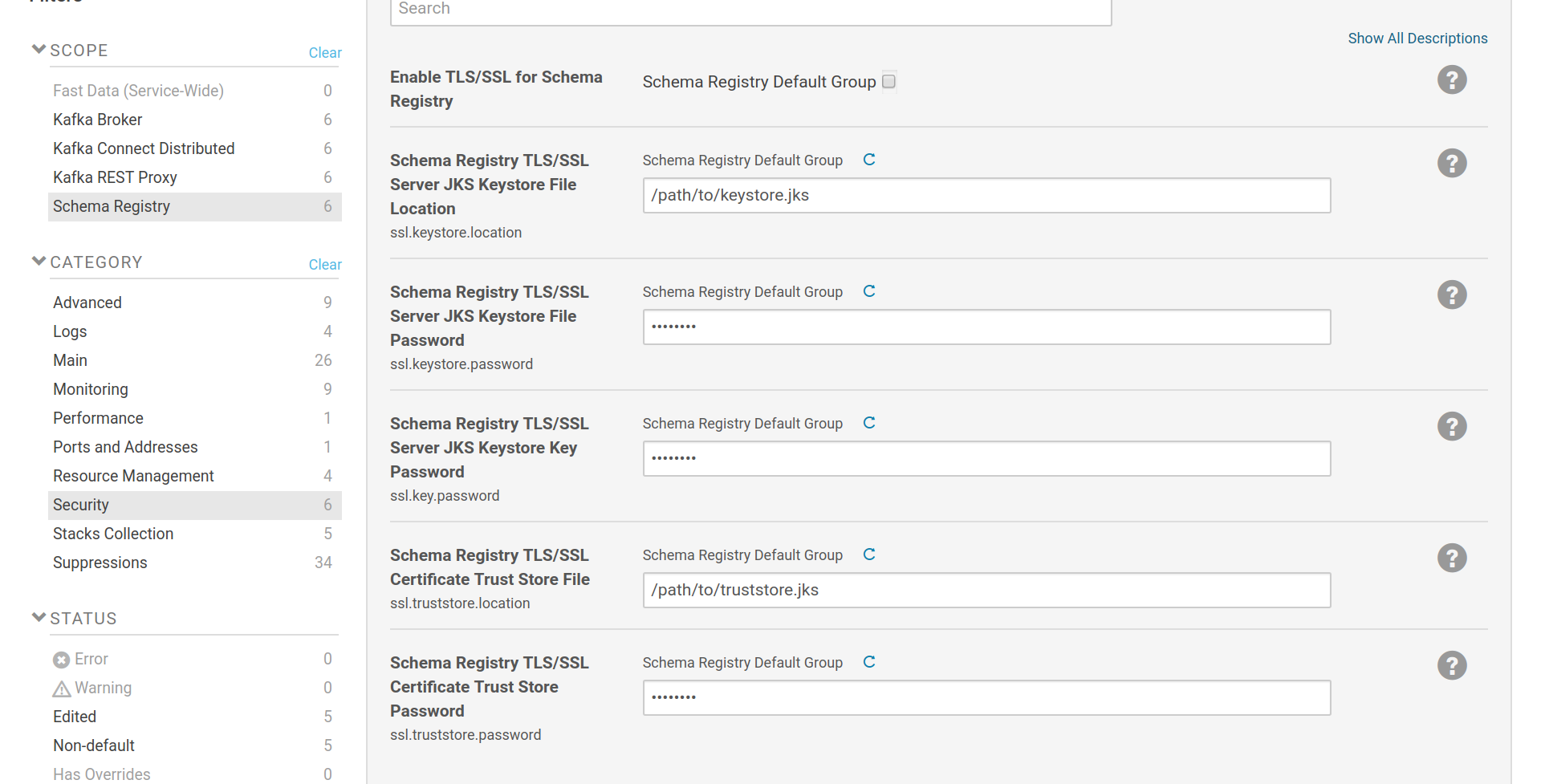
TLS/SSL setup for Schema Registry
If you want to test your setup, see Verify HTTPS Endpoints Authentication.
Important
If a truststore isn’t set, the Schema Registry will fall back to the system truststore. This truststore most likely contains certificates from trusted CAs like such as Comodo or Let’s Encrypt, so anyone with a certificate from these companies will be trusted.
| [6] | Due to limitations in Cloudera Manager, the same
TLS/SSL options are used for both Schema
Registry’s https listener and kafkastore
client. Separate configuration is possible:
instead of using the TLS/SSL setup fields in
Cloudera Manager, provide the ssl configuration
options for the listener and the kafkastore in
Schema Registry’s safety vale for
schema-registry.properties. See Confluent’s
Documentation on Schema Registry configuration
for more information on how to setup TLS/SSL
manually. |
1.3.4.3. Why a http listener is needed¶
There are a couple reasons for this requirement. The first is that due to a bug in the Schema Registry 4.0.x, the role will fail to start if no http listeners are set. In older versions whilst the role would start, Schema Registry instances couldn’t communicate via SSL in order to get the master-slave, high availability configuration of Schema Registry [GHI_1].
The second reason is that the Schema Registry can have service roles as clients: Kafka Connect workers and Kafka REST instances. Unfortunately support for the secure listener isn’t complete.
Kafka Connect and Kafka REST use the Schema registry to store and retrieve AVRO schemas. At the current Confluent/Kafka iteration (4.0.x) there isn’t a way to configure the Schema Registry client part for Kafka REST and Kafka Connect, thus falling to system defaults. This means that (a) they use the system’s truststore, so the Schema Registry CA certificate should be present there and (b) it is impossible to enable authentication via SSL client certificates. If these restrictions can be tolerated and you have only one Schema Registry instance, an only https setup is possible.
| [GHI_1] | Github Issue (confluentinc/schema-registry/issues/386) |
Note
If you also use the Fast Data Tools CSD, please note that Schema Registry UI does not yet support authentication via client certificate to the Registry. You can use the http listener for it instead or configure CORS for Schema Registry and disable proxying for Schema Registry UI.
1.3.4.4. Connection to the Brokers¶
Schema Registry supports all listener schemes provided by the brokers. By
default a broker listener is selected automatically in the order of
SASL_PLAINTEXT, PLAINTEXT, SASL_SSL and SSL. A specific listener can be
chosen either by setting the role specific option
kafkastore.security.protocol or the service wide option
fd.kafka.preferred.listener. If both aren’t set to AUTO, the former
will take precedence.
For connection to a plaintext listener, no additional configuration is needed.
For connection to a sasl_plaintext listener, the system wide
kerberos.auth.enable option should be enabled. For a ssl listener, the
TLS/SSL Configuration of the Schema Registry should be
completed. For a sasl_ssl listener the kerberos.auth.enable option is
needed as well as a SSL truststore should be set (or the system default will
be used).
1.3.5. Kafka REST Proxy¶
Kafka REST Proxy supports TLS/SSL for both transport encryption and client authentication for its REST endpoint. Its Kafka client part (consumer and producer) supports all authentication scenarios provided by the brokers.
As the Brokers and the Schema Registry, Kafka REST follows the concept of listeners, providing two schemes: http and https.
1.3.5.1. Listener Configuration¶
Kafka REST’s listener settings are part of the Fast Data service-wide scope.
Listeners can be enabled via fd.restproxy.listener.http and
fd.restproxy.listener.https. The https listener can be set to either
provide only transport encryption or to request authentication via SSL client
certificates as well.
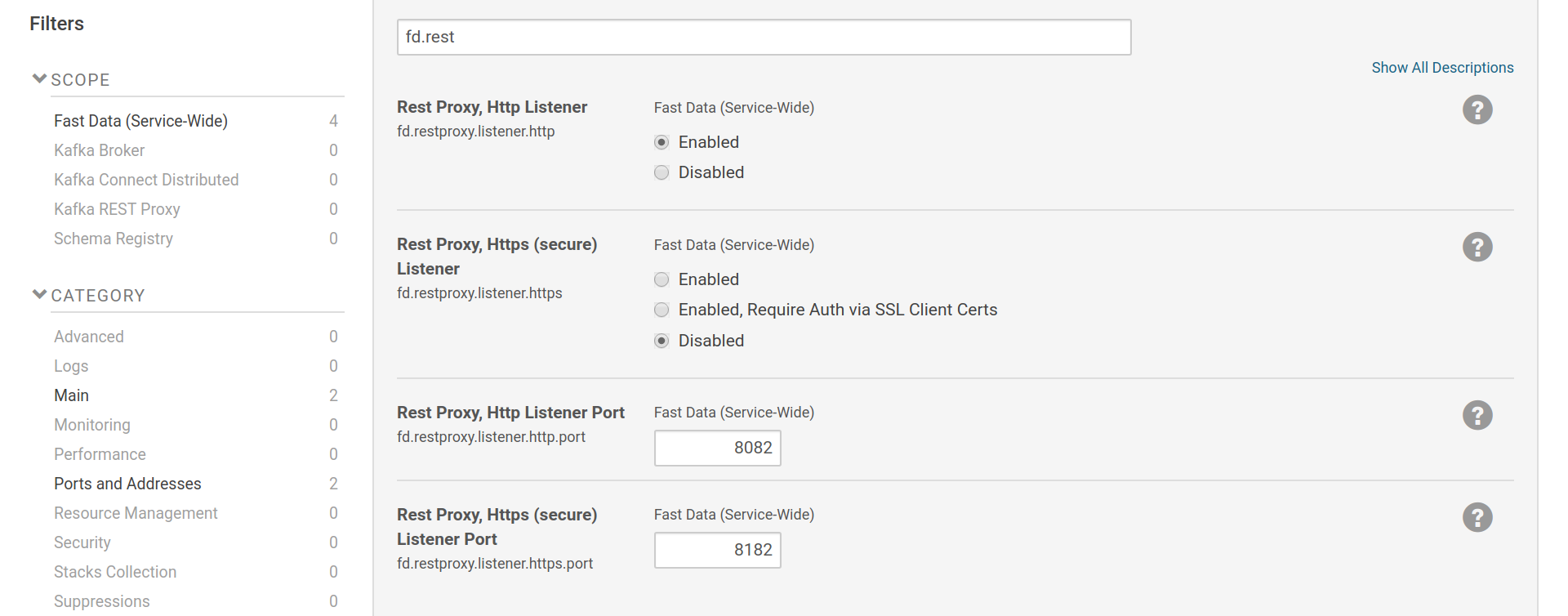
Settings for Kafka REST listeners
Note
If you also use the Fast Data Tools CSD, please note that Kafka Topics UI does not yet support authentication via client certificate to the REST Proxy. You can use the http listener or configure CORS on Kafka REST and disable proxying in Kafka Topics UI.
1.3.5.2. TLS/SSL Configuration¶
The SSL configuration options are provided by Cloudera Manager and are similar to any other role in CM that uses SSL. The SSL settings for the listener part are common with the settings for the client (consumer/producer) part. This can be overriden by a safety valve [7] .
The keystore settings (ssl.keystore.location, ssl.keystore.password,
ssl.key.password) are used to set the location and passwords of a java
keystore file which contains a SSL key and certificate pair. This pair is used
by the https listener, as well as in the authentication process when Kafka REST
is set to communicate with the Brokers via SSL client certificate
authentication. The truststore settings (ssl.truststore.location,
ssl.truststore.password) are used to set the location and password of a java
keystore file which contains one or more certificates from trusted CAs. If client authentication via SSL certificates is
enabled, the certificate provided by the client will be checked against these
CAs. If set to communicate with the brokers via SSL, the kafka client will
verify the certificates provided by the brokers against the CAs in its
truststore. Keystore and truststore can be the same file. Please note that the
option Enable TLS/SSL for Kafka REST Proxy isn’t used. It is provided by
Cloudera Manager but the way Fast Data makes use of SSL, does not require its
setting.
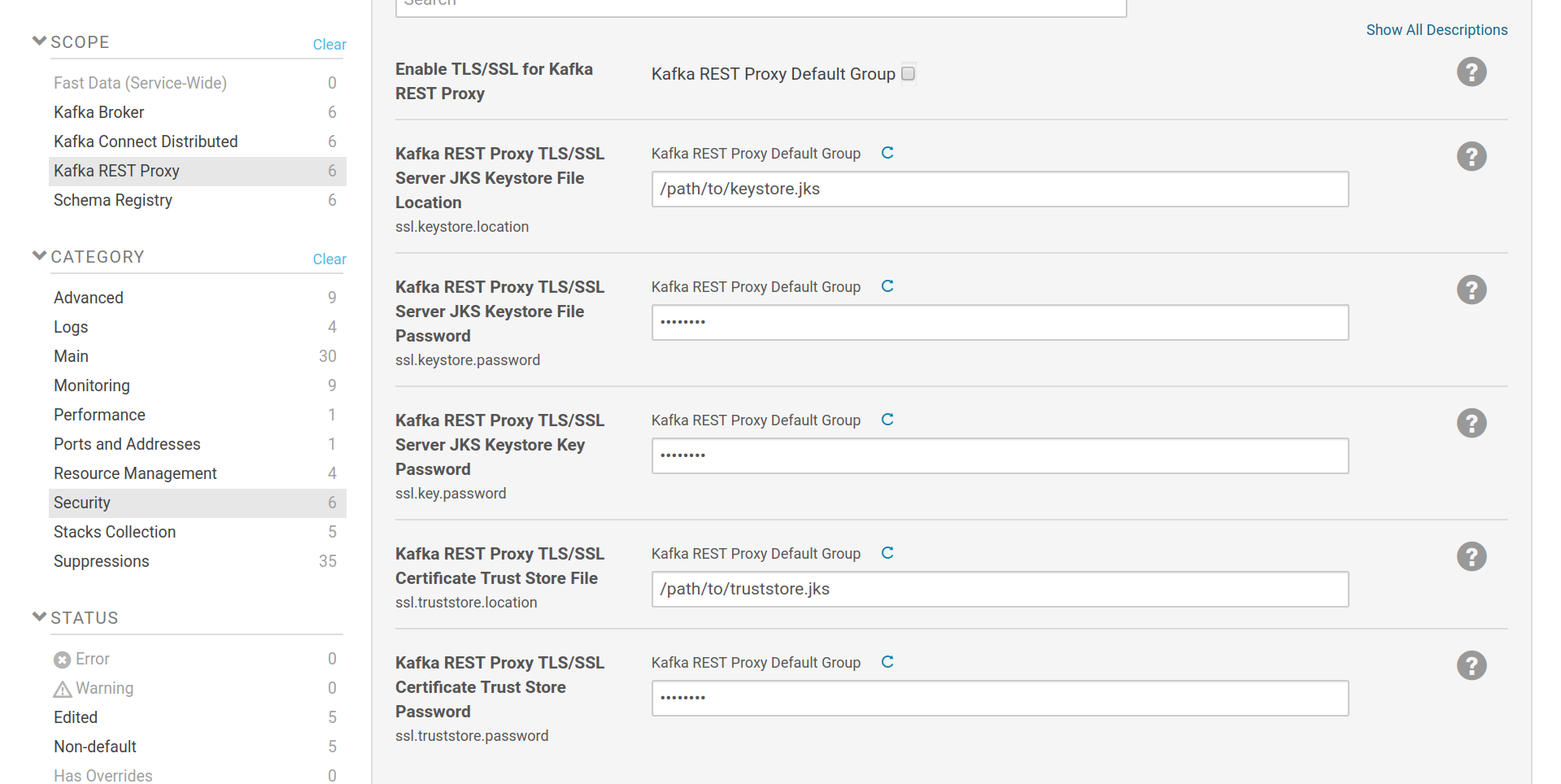
TLS/SSL setup for Kafka REST
If you want to test your setup, see Verify HTTPS Endpoints Authentication.
Important
If a truststore isn’t set, Kafka REST will fall back to the system truststore. This truststore most likely contains certificates from trusted CAs like such as Comodo or Let’s Encrypt, so anyone with a certificate from these companies will be trusted.
| [7] | Due to limitations in Cloudera Manager, the same
TLS/SSL options are used for both Kafka REST’s https
listener and kafka client. Separate configuration is
possible: instead of using the TLS/SSL setup fields in
Cloudera Manager, provide the ssl configuration
options for the listener and the kafka client in Kafka
REST’s safety vale for kafka-rest.properties. See
Confluent’s Documentation on Kafka REST security
configuration for more information on how to setup
TLS/SSL manually. |
1.3.5.3. Connection to the Brokers¶
Kafka REST supports all listener schemes provided by the brokers. By
default a broker listener is selected automatically in the order of
SASL_PLAINTEXT, PLAINTEXT, SASL_SSL and SSL. A specific listener can be
chosen either by setting the role specific option
client.security.protocol or the service wide option
fd.kafka.preferred.listener. If both aren’t set to AUTO, the former
will take precedence.
For connection to a plaintext listener, no additional configuration is needed.
For connection to a sasl_plaintext listener, the system wide
kerberos.auth.enable option should be enabled. For a ssl listener, the
TLS/SSL Configuration of the Kafka REST should be
completed. For a sasl_ssl listener the kerberos.auth.enable option is
needed as well as a SSL truststore should be set (or the system default will
be used).
1.3.6. Kafka Connect¶
Since Kafka 1.1, the Connect worker supports TLS/SSL for both transport encryption and client authentication for its REST endpoint. Its Kafka client part (consumer and producer) supports all authentication scenarios provided by the brokers.
As the Brokers and the Schema Registry, Kafka Connect since version 1.1 follows
the concept of listeners, providing two schemes: http and https with a
small twist; the host should be set explicitly to an address that can be
resolved by clients instead of a listen-all address, such as 0.0.0.0.
Of course, the Fast Data CSD will take care of this automatically for you.
1.3.6.1. Listener Configuration¶
Kafka Connect worker’s listener settings are part of the Fast Data service-wide scope.
Listeners can be enabled via fd.connect.listener.http and
fd.connect.listener.https. The https listener can be set to either
provide only transport encryption or to request/require authentication via SSL client
certificates as well.
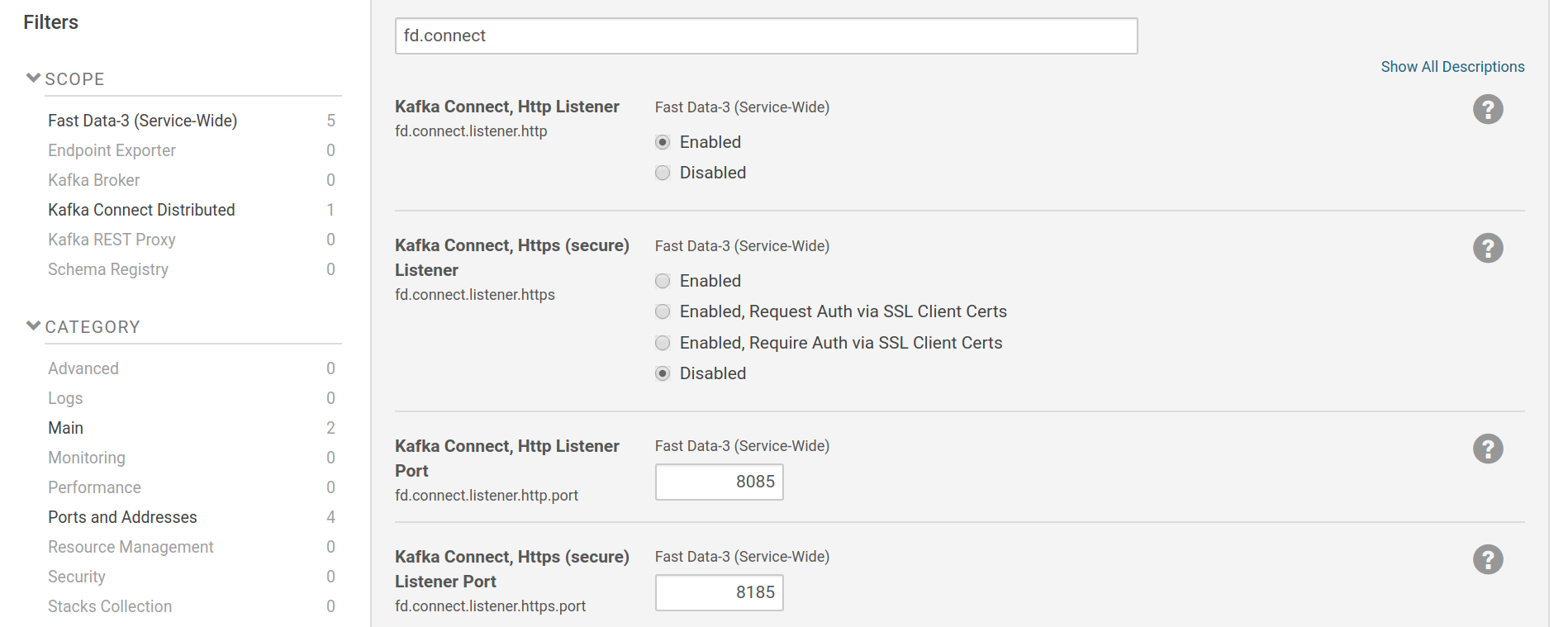
Settings for Kafka Connect listeners
Note
If you also use the Fast Data Tools CSD, please note that Kafka Connect UI does not yet support authentication via client certificate to the Connect worker. If authentication via https is required for external clients, you can setup a http listener that will be available only internally in your cluster (via a firewall rule maybe) for use by Kafka Connect UI.
1.3.6.2. TLS/SSL Configuration¶
The SSL configuration options are provided by Cloudera Manager and are similar to any other role in CM that uses SSL. These options are used for the Kafka consumer and producer parts of Kafka Connect workers when they have to connect to a broker listener that uses SSL, as well as for the REST endpoint (listener).
Kafka Connect workers have three different parts that interact with the brokers and support distinct configuration: the worker itself (stores its configuration in Kafka), the consumer part (used by sink connectors) and the producer part (used by source connectors). The SSL settings for all three parts are common. This can be overriden by a safety valve [8] .
The keystore settings (ssl.keystore.location, ssl.keystore.password,
ssl.key.password) are used to set the location and passwords of a java
keystore file which contains a SSL key and certificate pair. This pair is used
in the authentication process when Kafka Connect is set to communicate with the
Brokers via SSL client certificate authentication. The truststore settings
(ssl.truststore.location, ssl.truststore.password) are used to set the
location and password of a java keystore file which contains one or more
certificates from trusted CAs. The Connect
worker will verify the certificates provided by the brokers against the CAs in
its truststore. Keystore and truststore can be the same file. Please note that
the option Enable TLS/SSL for Kafka REST Proxy isn’t used. It is provided by
Cloudera Manager but the way Fast Data makes use of SSL, does not require its
setting.
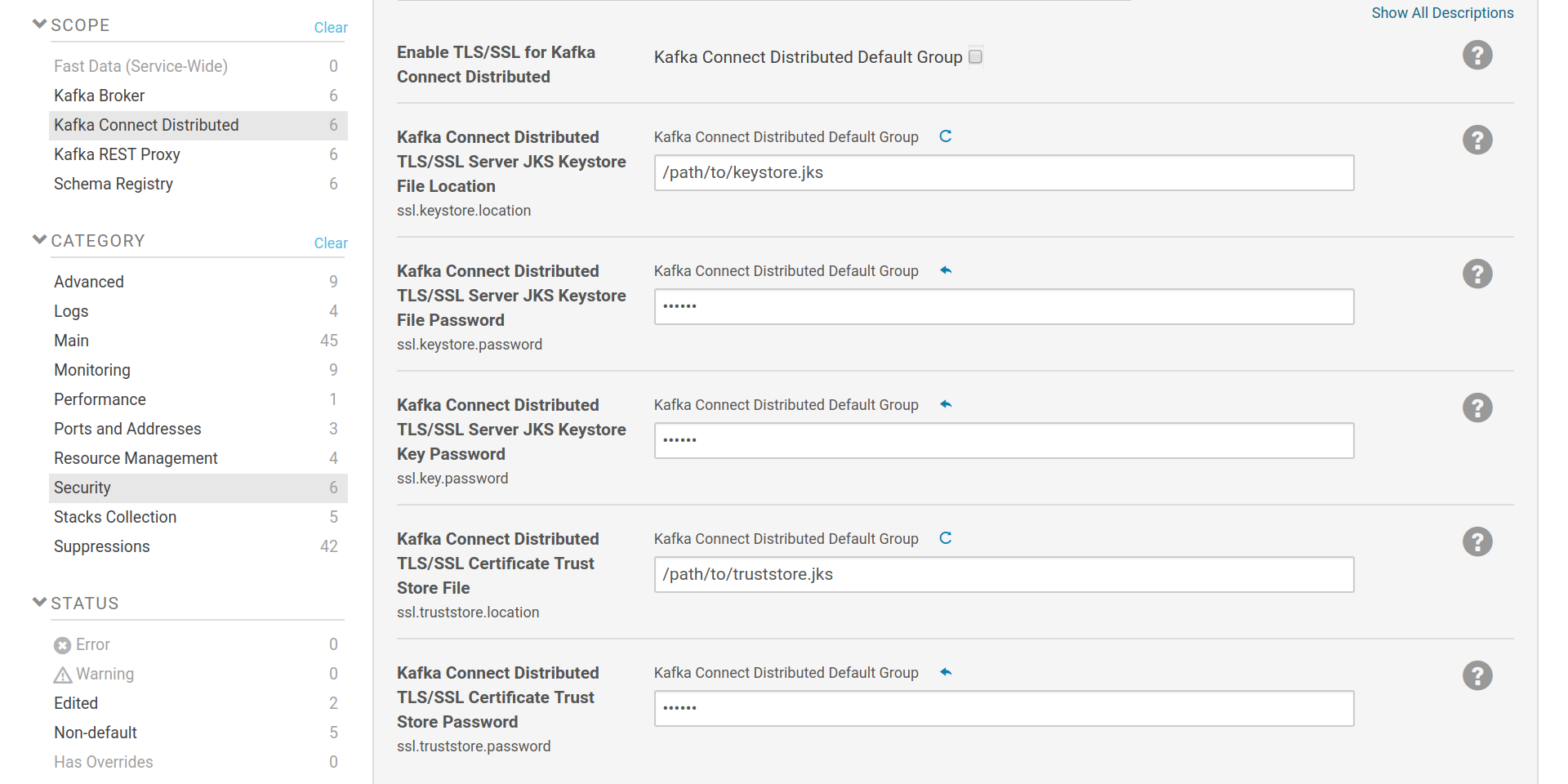
TLS/SSL setup for Kafka Connect
| [8] | Due to limitations in Cloudera Manager, the same TLS/SSL
options are used for all: Kafka Connect’s worker,
producer and consumer, Kafka Connect REST
endpoint. Separate configuration should be possible:
instead of using the TLS/SSL setup fields in Cloudera
Manager, provide the ssl configuration options for the
worker, the producer and the consumer in Kafka Connect’s
safety valve for worker.properties.
for more information on how to setup TLS/SSL
manually see Confluent’s Documentation on Kafka Connect security,
Kafka Connect config documentation and Kafka Connect SSL support to REST interface (KIP). |
1.3.6.3. Connection to the Brokers¶
Kafka Connect supports all listener schemes provided by the brokers. By default
a broker listener is selected automatically in the order of SASL_PLAINTEXT,
PLAINTEXT, SASL_SSL and SSL. A specific listener can be chosen either by
setting the role specific option security.protocol or the service wide
option fd.kafka.preferred.listener. If both aren’t set to AUTO, the
former will take precedence.
For connection to a plaintext listener, no additional configuration is needed.
For connection to a sasl_plaintext listener, the system wide
kerberos.auth.enable option should be enabled. For a ssl listener, the
TLS/SSL Configuration of Kafka Connect should be completed. For a
sasl_ssl listener the kerberos.auth.enable option is needed as well as a
SSL truststore should be set (or the system default will be used).
1.3.7. Additional Topics¶
1.3.7.1. Advanced Setups with Overrides¶
The options provided from Fast Data in Cloudera Manager UI may not cover certain advanced setup scenarios. Some of these scenarios, like distinct SSL settings for various parts of a role, are already mentioned in their respective sections.
They way to work around such UI limitations, is to use the safety valve of each role to directly set the needed configuration options. We try hard to make sure that such overrides are detected and accepted by the roles’ setup scripts.
If help is needed to implement such an advanced scenario or a bug is discovered, please contact us.
1.3.7.2. Verify Kerberos¶
To verify that Kerberos authorization works, from a node of your cluster you may obtain a ticket-granting ticket from Kerberos and run a short performance test.
First create a JAAS configuration file that contains your Kerberos principal:
KafkaClient {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useTicketCache=true
serviceName="kafka"
principal="user@DOMAIN";
};
Client {
com.sun.security.auth.module.Krb5LoginModule required
useTicketCache=true
principal="user@DOMAIN";
};
Then proceed to obtain your TGT via kinit [9], create a test topic [10] and run the performance test:
$ kinit user@DOMAIN
$ kafka-topics \
--zookeeper zk:2181/fastdata \
--create \
--topic test-krb \
--partitions 9 \
--replication-factor 3
$ KAFKA_OPTS=-Djava.security.auth.login.config=/path/to/jaas.conf kafka-producer-perf-test \
--topic test-krb \
--throughput 1000 \
--record-size 1000 \
--num-records 5000 \
--producer-props \
bootstrap.servers=broker1:9092,broker2:9092,broker3:9092 \
security.protocol=SASL_PLAINTEXT
$ kafka-topics --zookeeper zk:2181/fastdata --delete --topic test-krb
| [9] | The procedure to obtain a Kerberos TGT is outside of the scope of this
document. Usually the kinit command is enough. Consult your
cluster administrator in case it doesn’t work. |
| [10] | You may notice that instead of exporting the KAFKA_OPTS variable
we set it explicitly only for the kafka-producer-perf-test. Be
careful because if you set it for your shell, then kafka-topics
will use Kerberos to login to Zookeeper and will write SASL protected
topics that your brokers can’t access. |
1.3.7.3. Verify Brokers SSL Authentication¶
As with Kerberos, you can use a SSL keystore, a SSL truststore and run a small performance test to verify your brokers work as expected.
Once you obtain your keystore and truststore, create a topic and the test:
$ kafka-topics \
--zookeeper zk:2181/fastdata \
--create \
--topic test-tls \ --partitions 9 \
--replication-factor 3
$ kafka-producer-perf-test \
--topic test-tls \
--throughput 1000 \
--record-size 1000 \
--num-records 5000 \
--producer-props \
bootstrap.servers=broker1:9093,broker2:9093,broker3:9093 \
security.protocol=SSL \
ssl.keystore.location=/path/to/keystore.jks \
ssl.keystore.password=changeit \
ssl.key.password=changeit \
ssl.truststore.location=/path/to/truststore.jks \
ssl.truststore.password=changeit
$ kafka-topics --zookeeper zk:2181/fastdata --delete --topic test-tls
1.3.7.4. Verify HTTPS Endpoints Authentication¶
To verify your https listeners from Schema Registry or Kafka REST Proxy you will need a key-certificate pair in PEM format [11] and curl.
To verify Schema Registry once you obtain your PEM files, first verify that it doesn’t permit connections without autentication:
$ curl https://schema.registry.url:8081
Then use your PEM keys to verify that authentication works:
$ curl --cert certificate.pem --key key.pem https://schema.registry.url:8081
The same procedure applies to Kafka REST Proxy:
$ curl https://kafka.rest.url:8082
$ curl --cert certificate.pem --key key.pem https://kafka.rest.url:8082
| [11] | It is out of the scope of this document to explain the procedure to create PEM credentials. Please consult with your cluster administrator. |